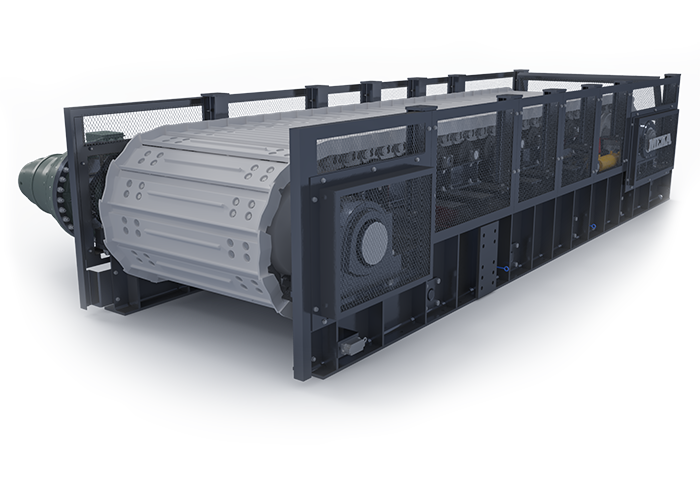
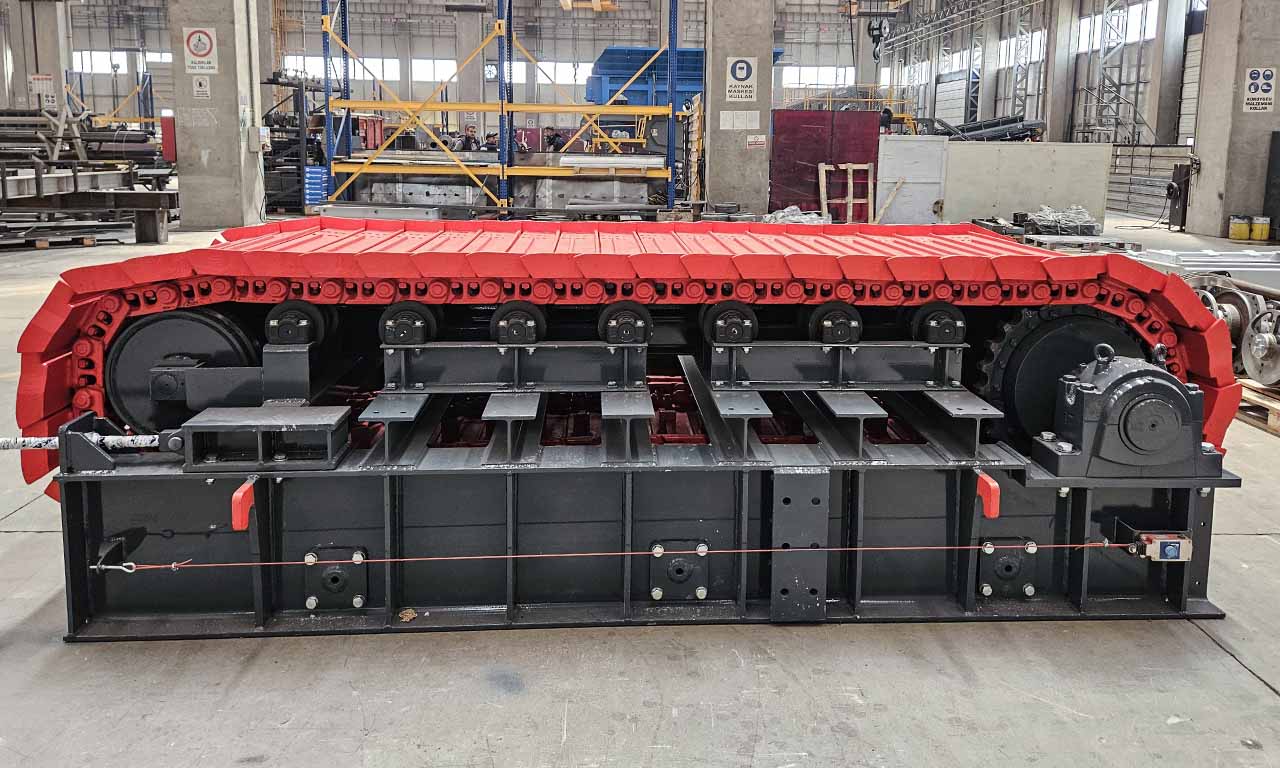
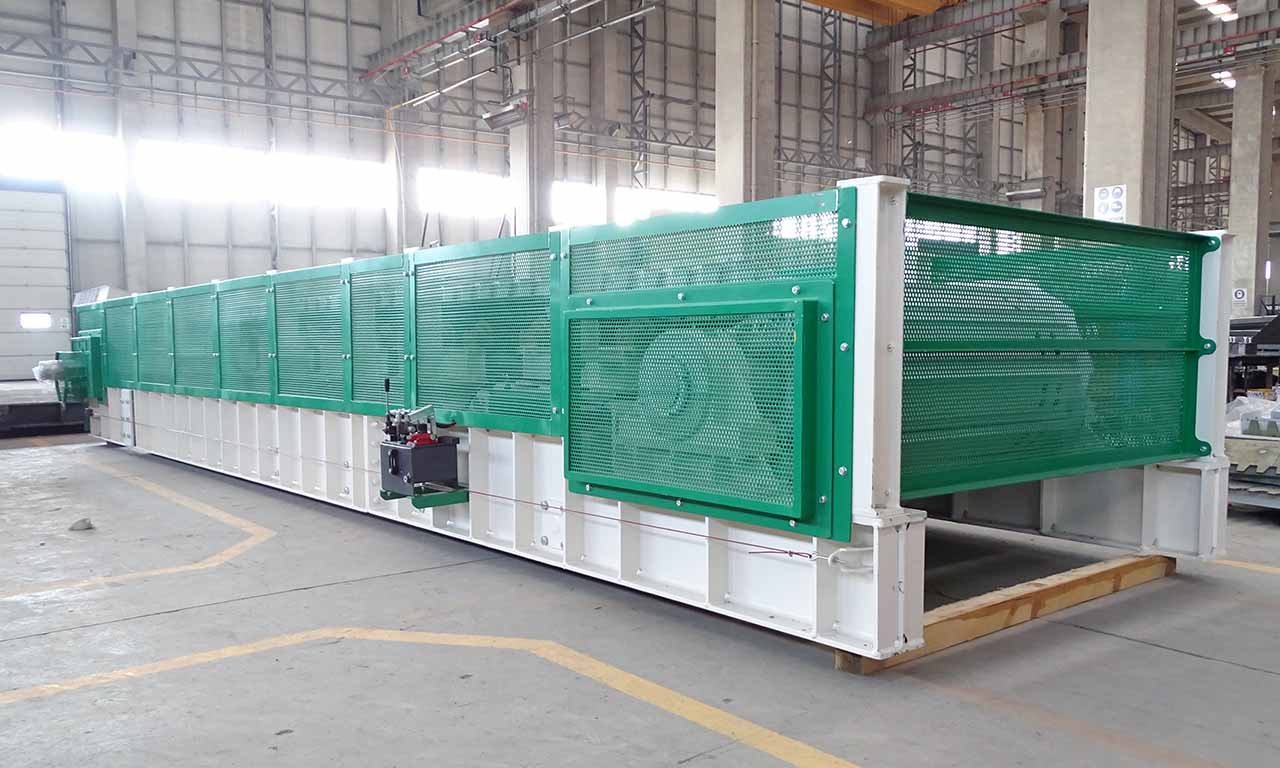
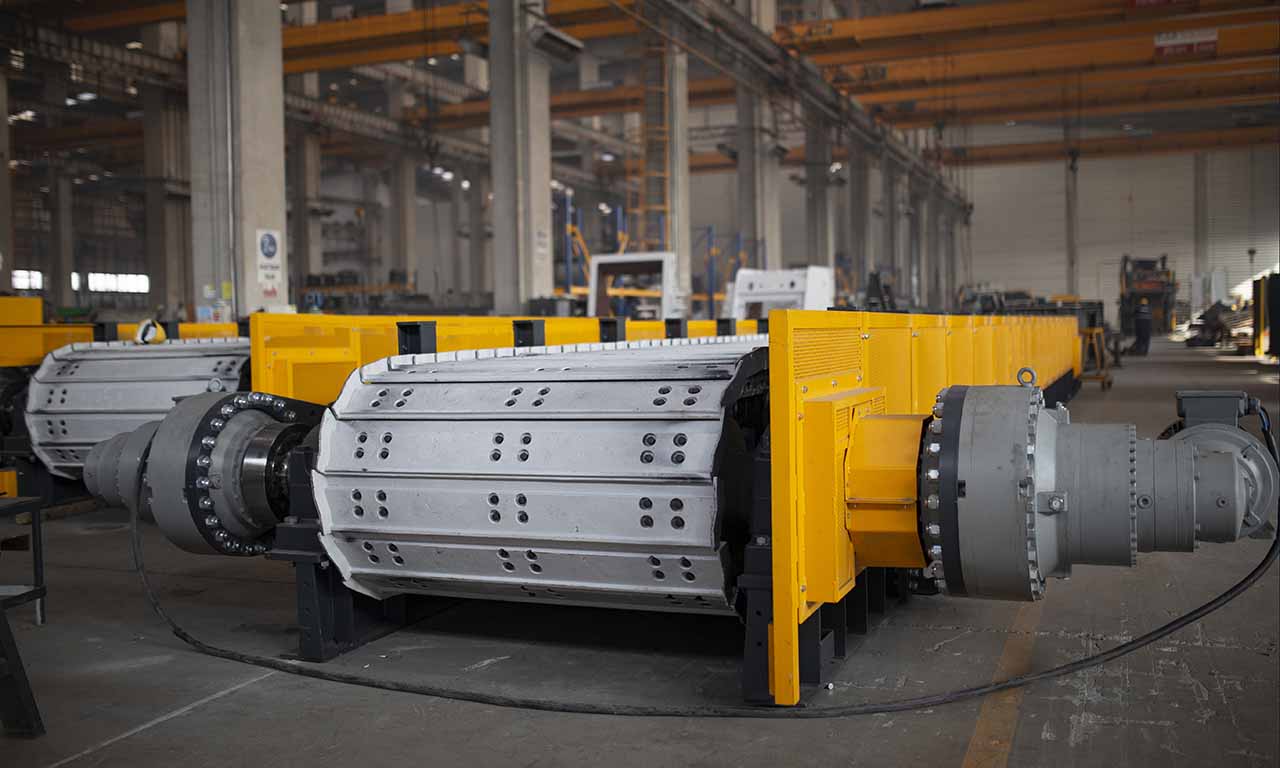
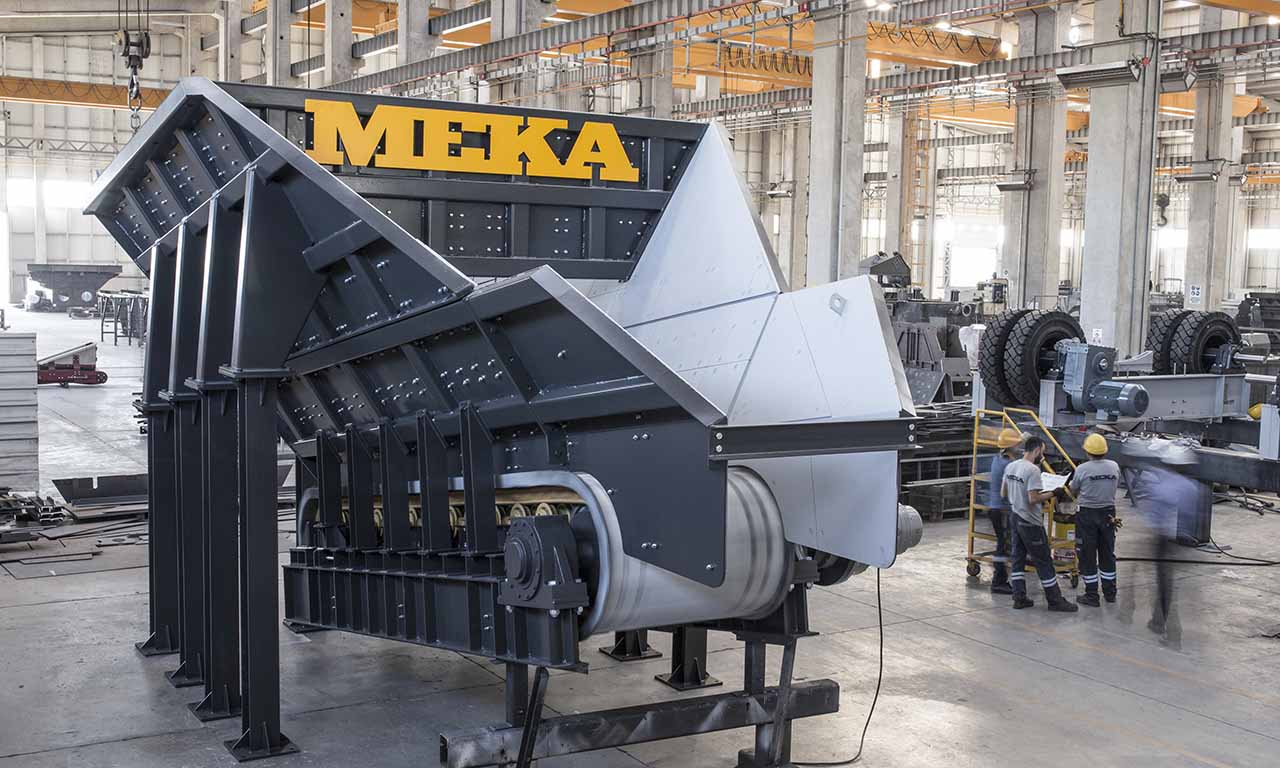
Alimentateur à Tablier Métallique Galérie
Performance inégalée dans l’alimentation de matériaux difficiles
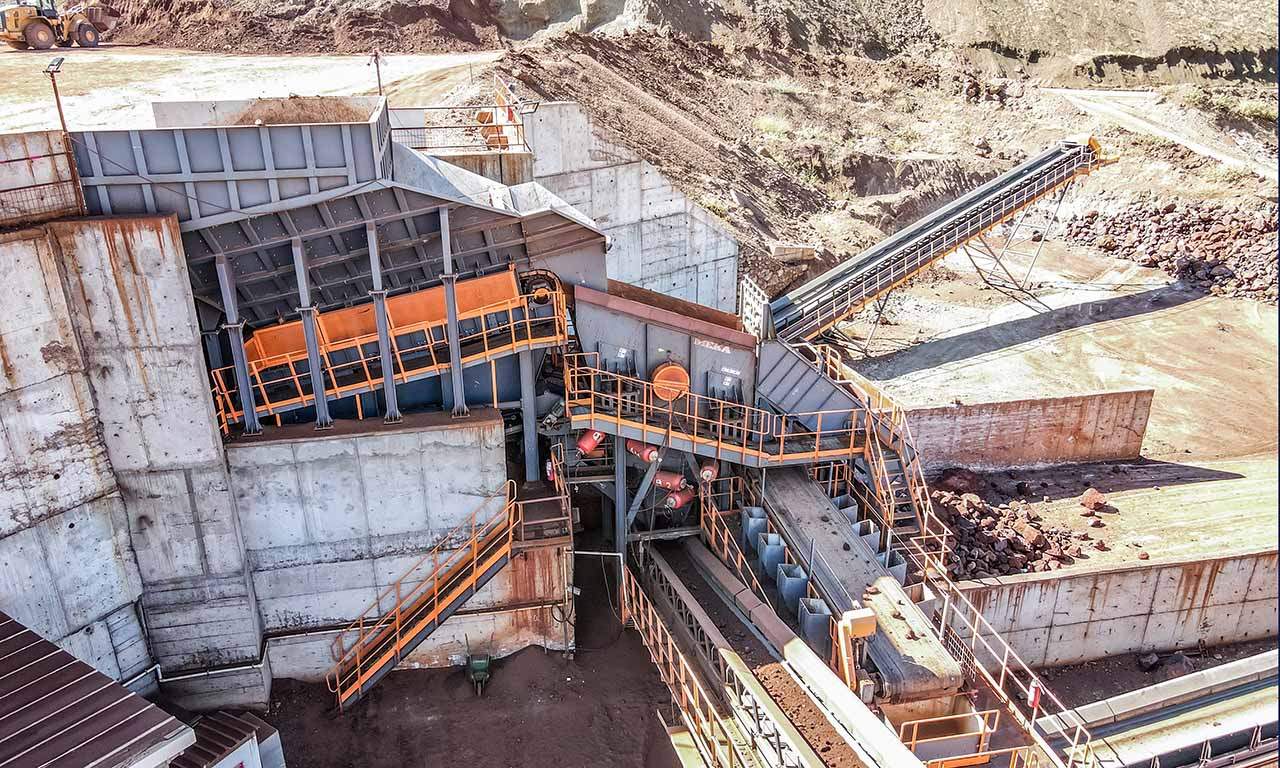
Dans les carrières, on rencontre souvent des veines rocheuses dont l’alimentation devient problématique pendant les mois d’hiver pluvieux. Les alimentateurs à tablier métallique sont la solution idéale pour ces matériaux.
Bien que leur coût d’investissement soit plus élevé que celui d’autres alimentateurs, leur capacité à fonctionner dans toutes les conditions en fait un choix privilégié. Pour les matériaux fins, humides et collants, un alimentateur à disques (Wobbler) de type MWF ou un alimentateur vibrant à grille peut être installé après l’alimentateur à tablier afin de séparer les matériaux indésirables avant le concasseur et d’alimenter celui-ci en matériaux propres, garantissant ainsi l’efficacité.
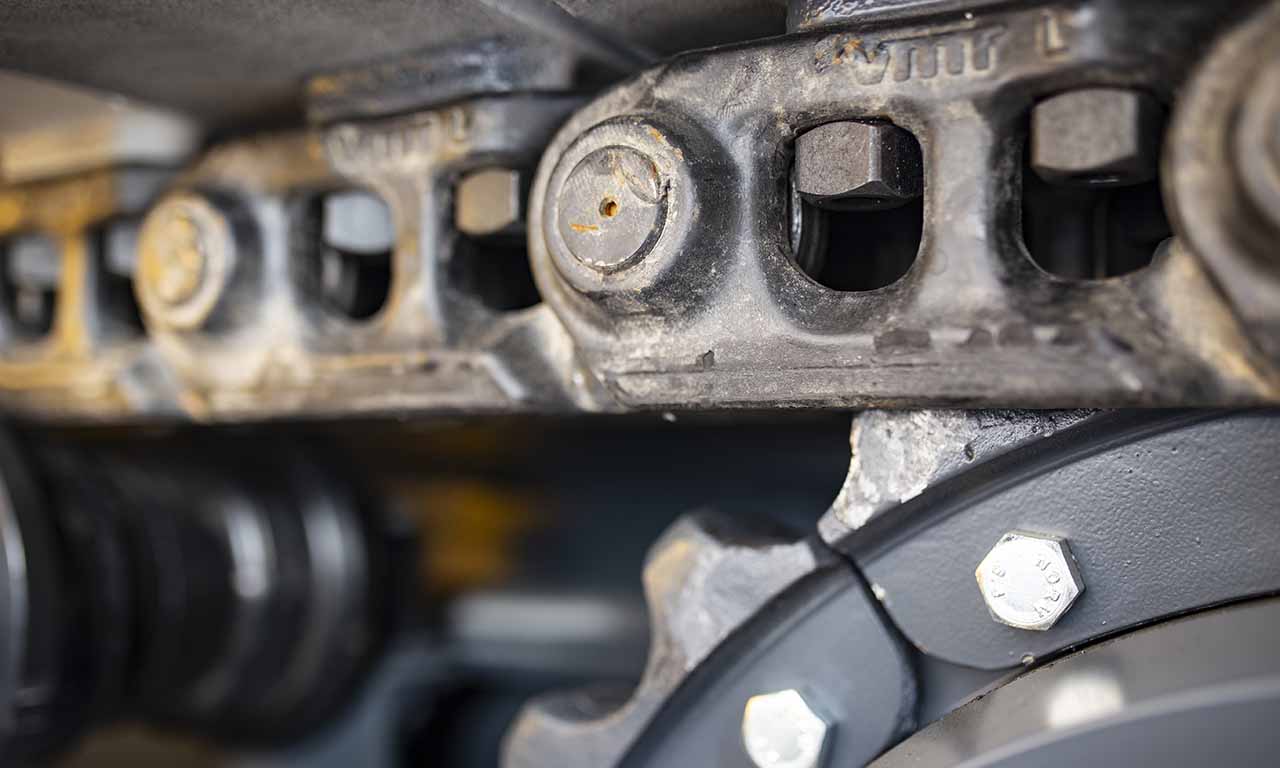
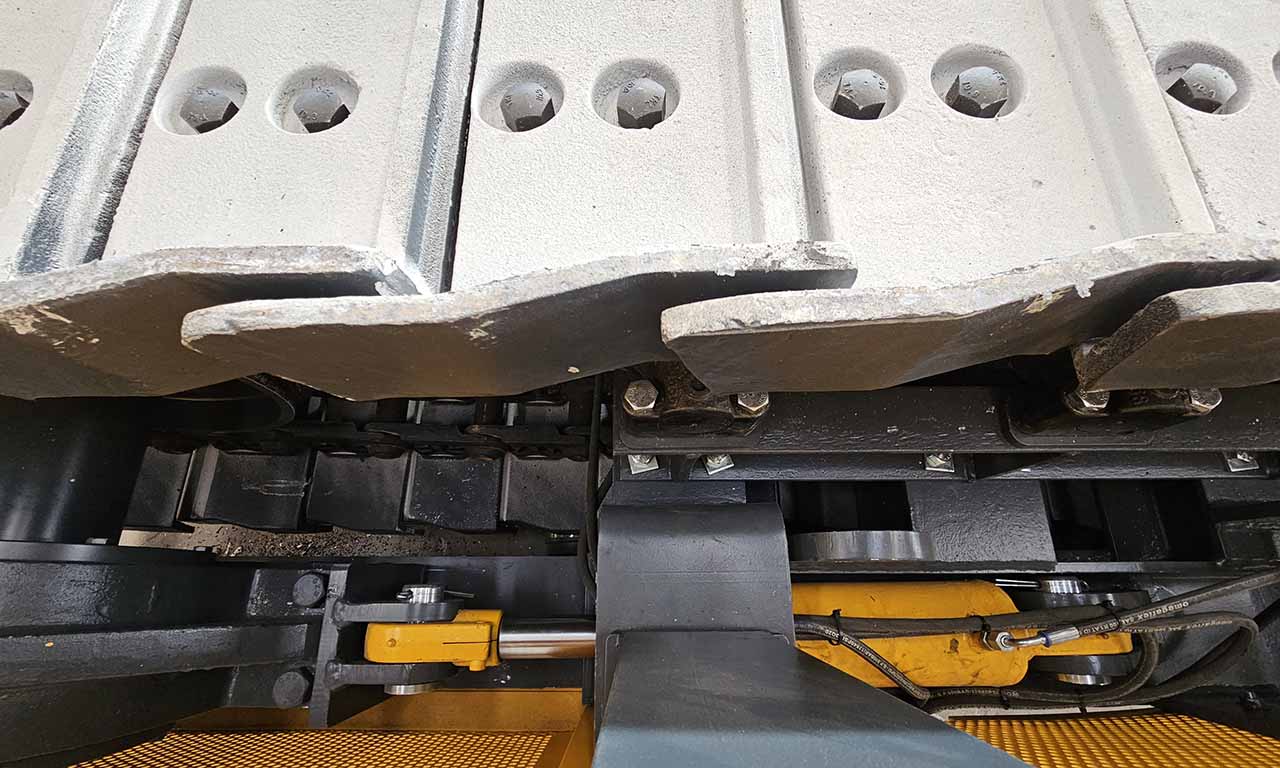
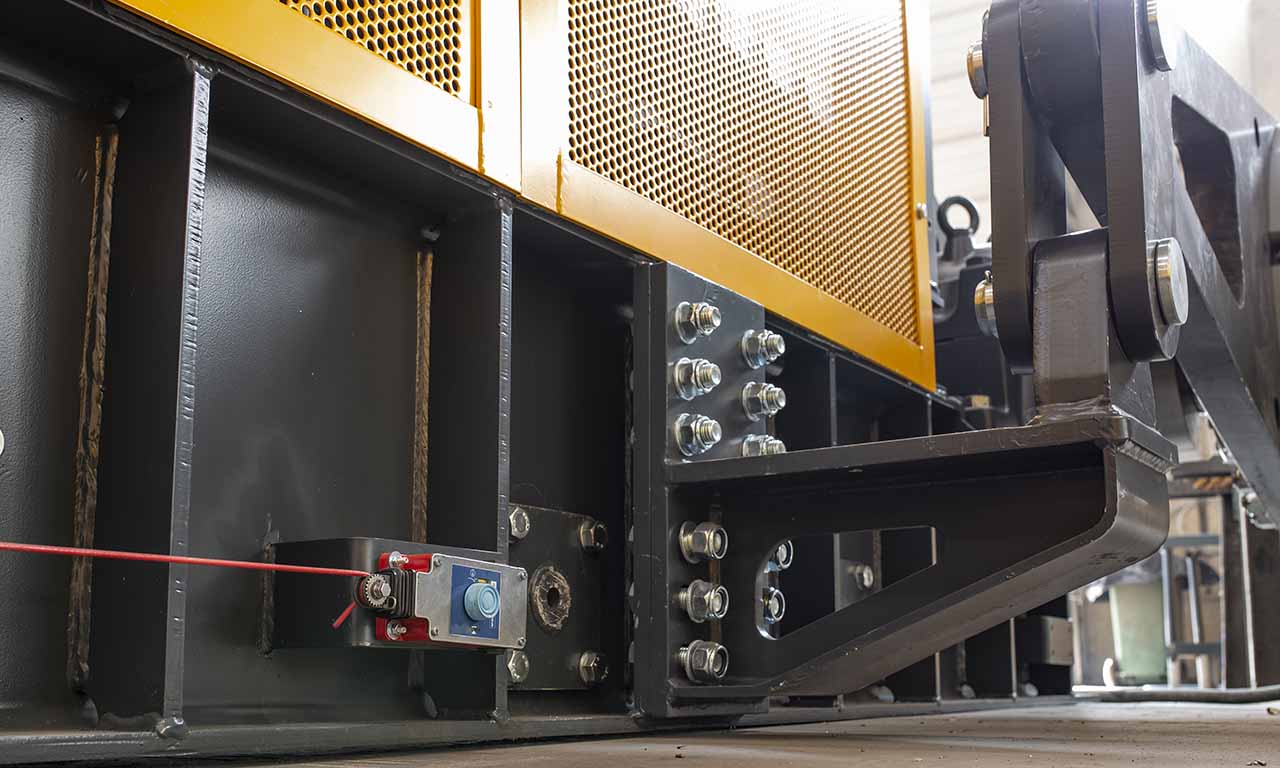
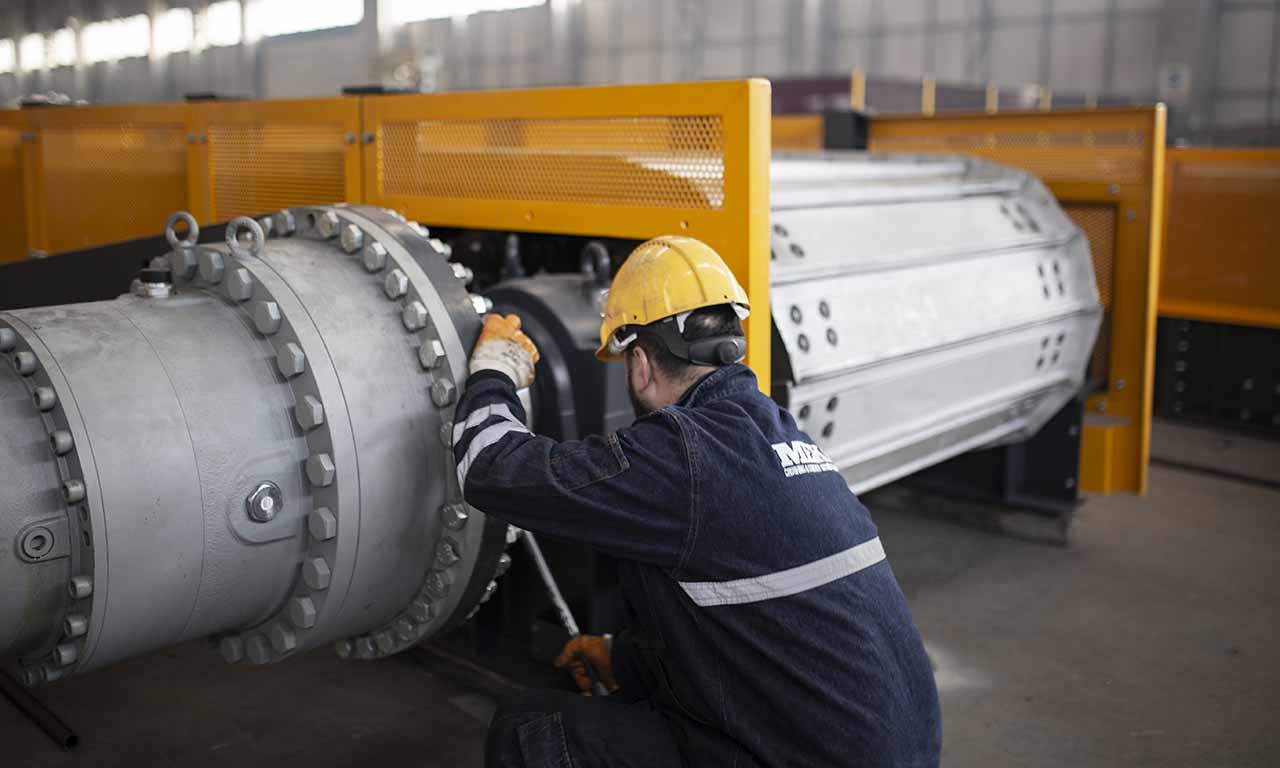
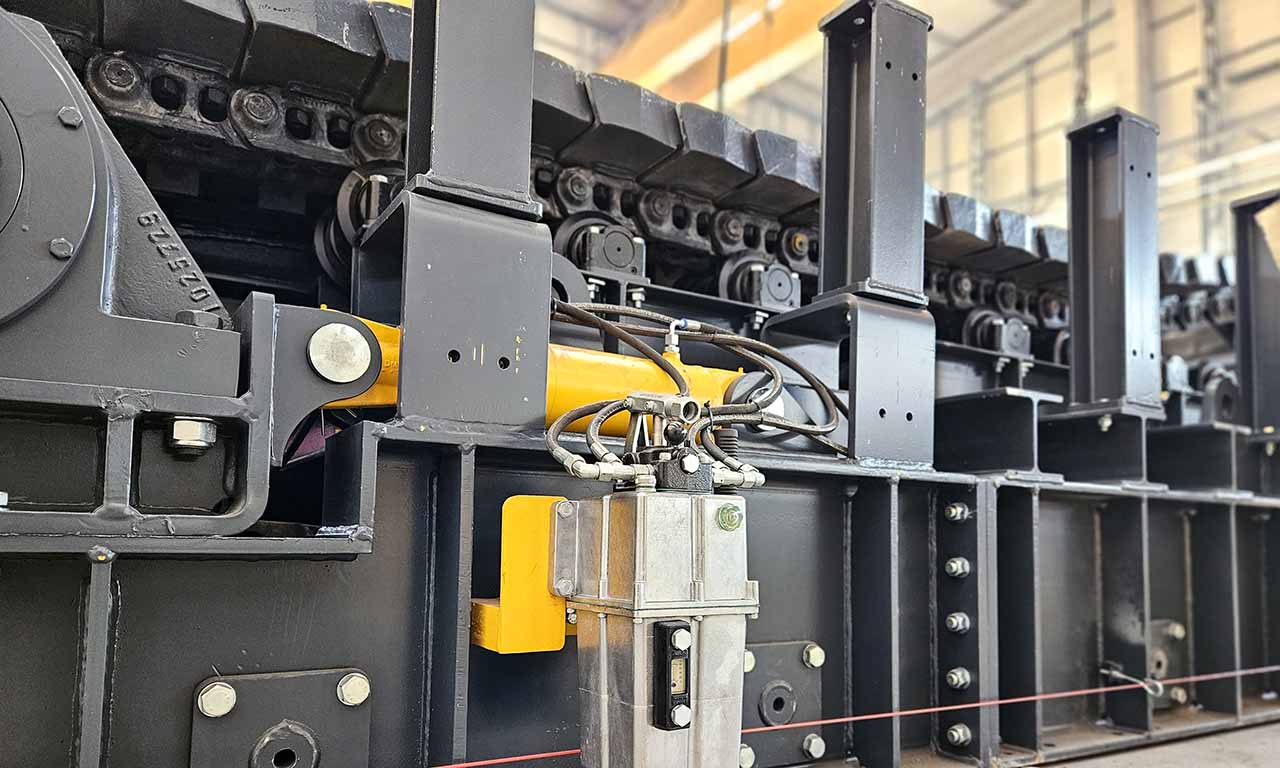
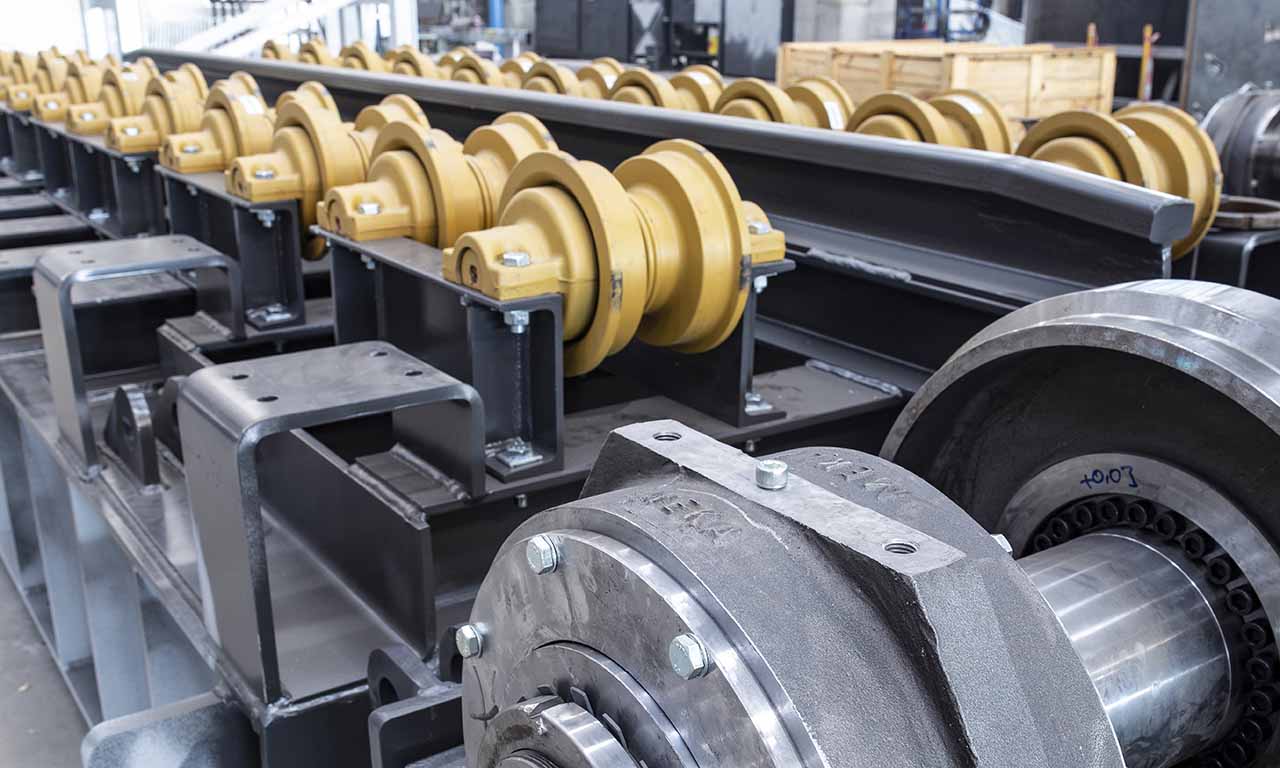
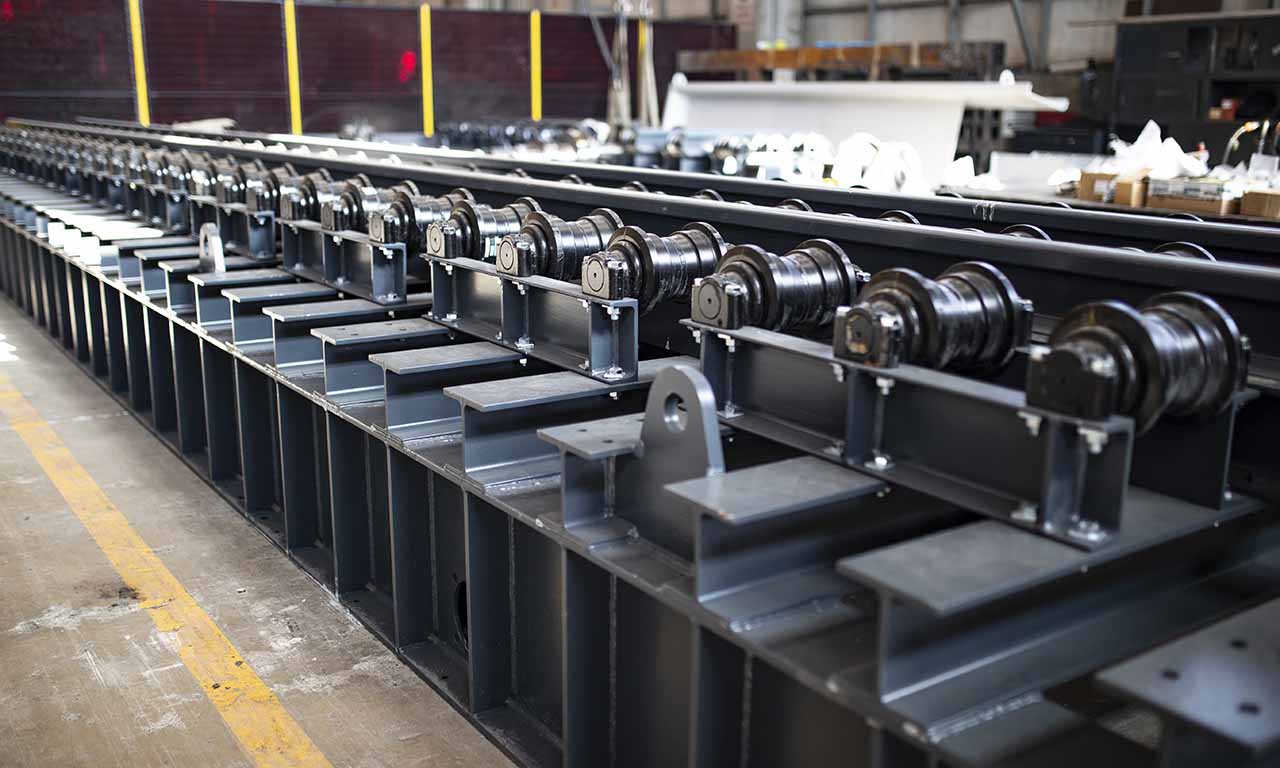
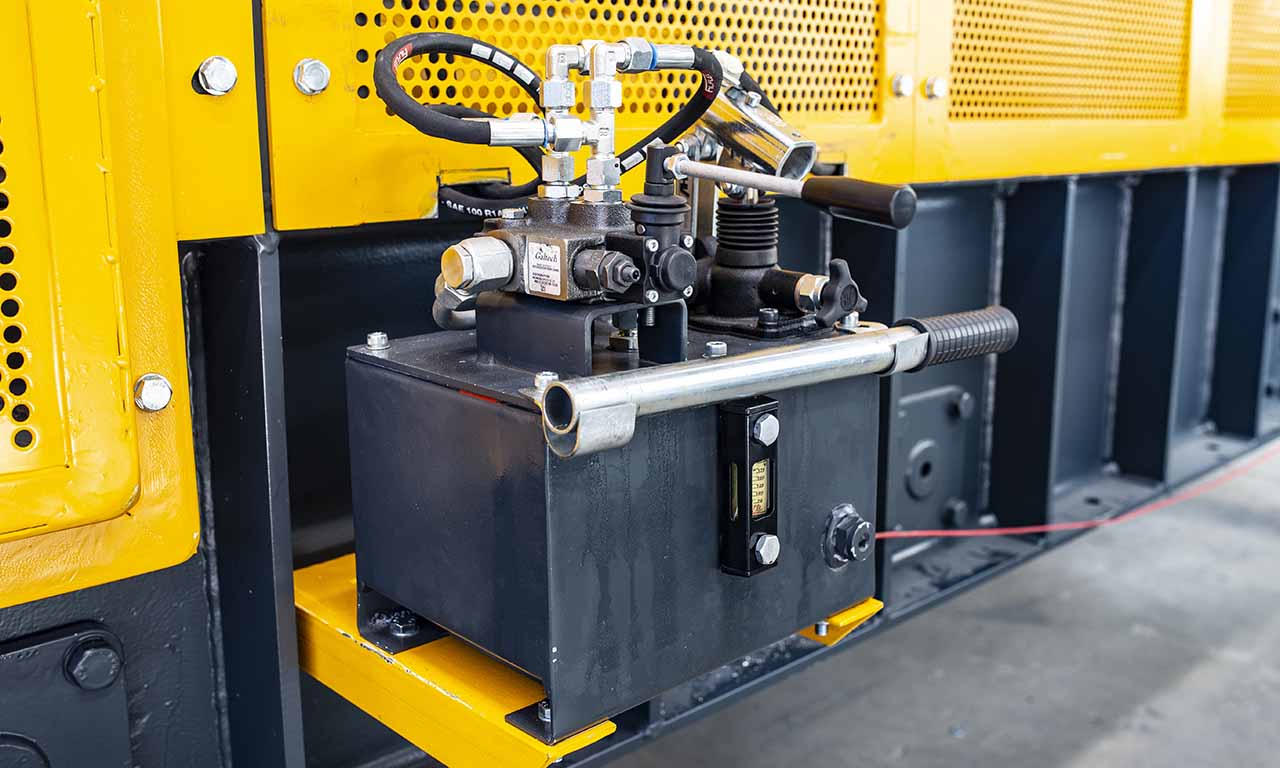
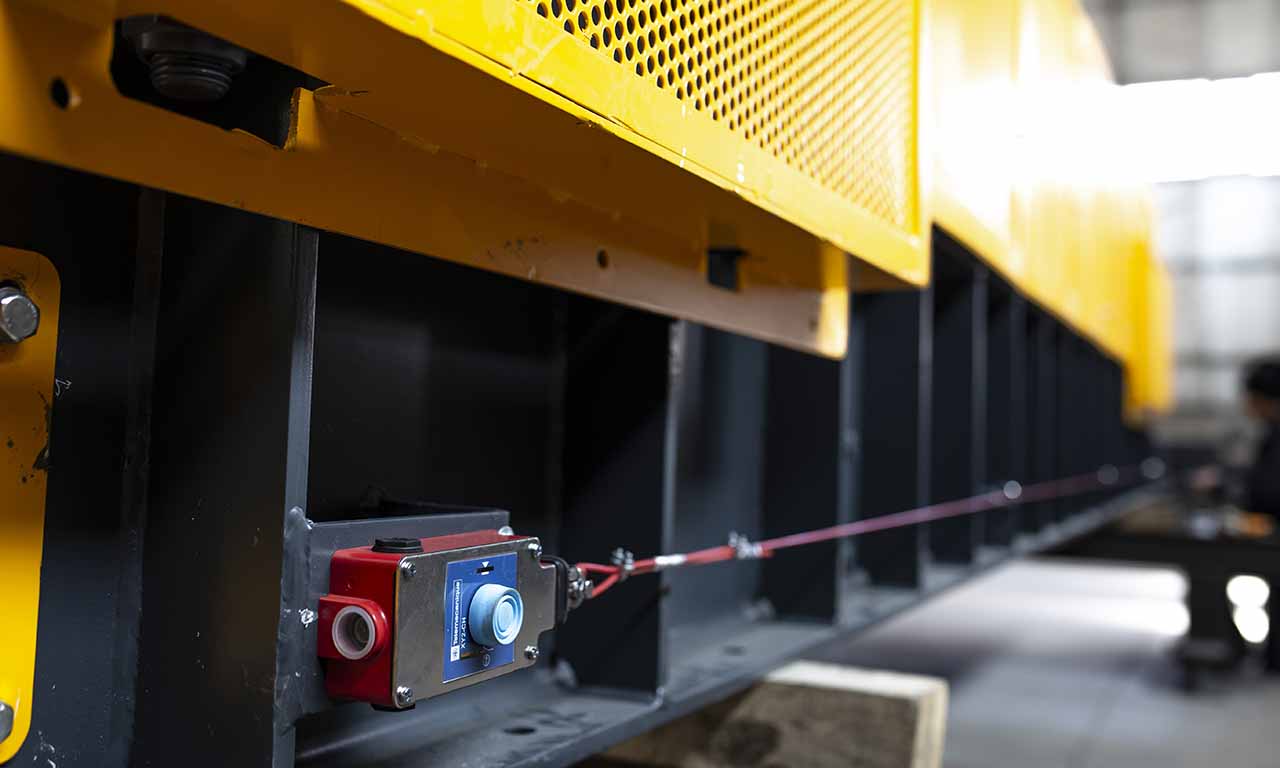
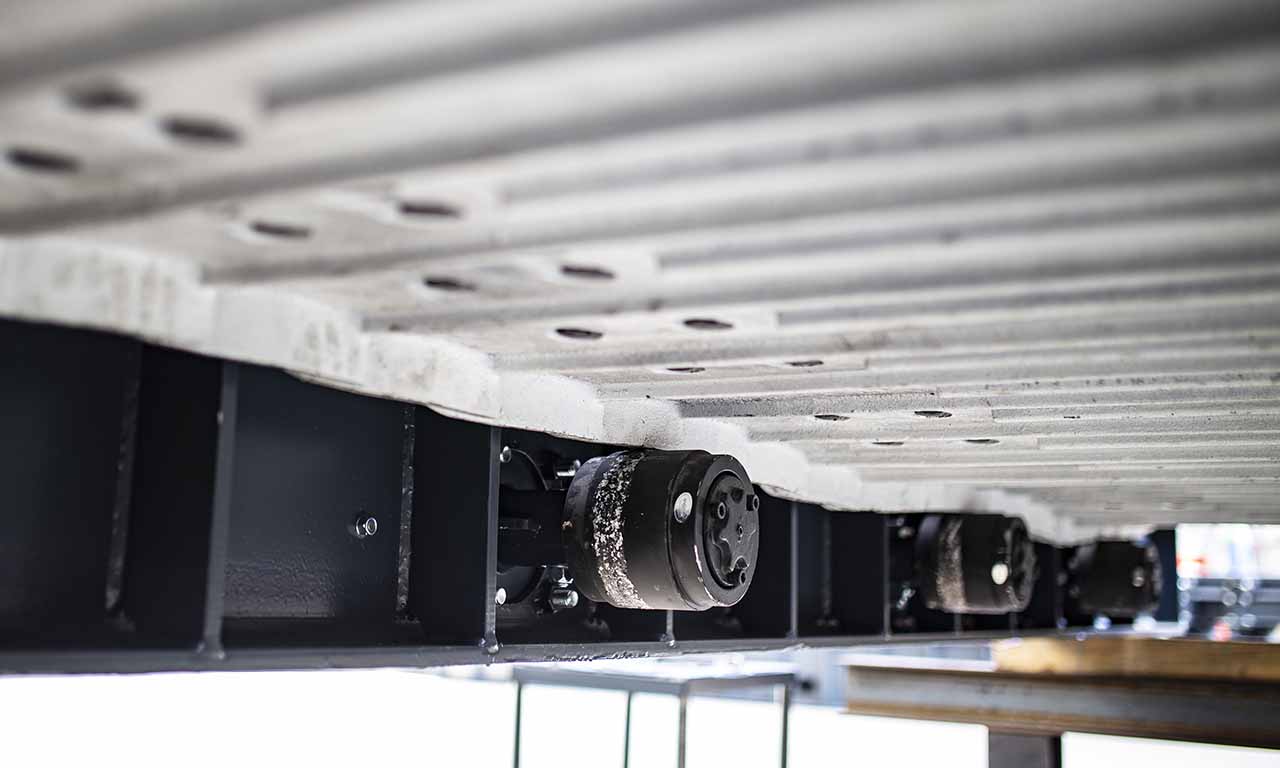
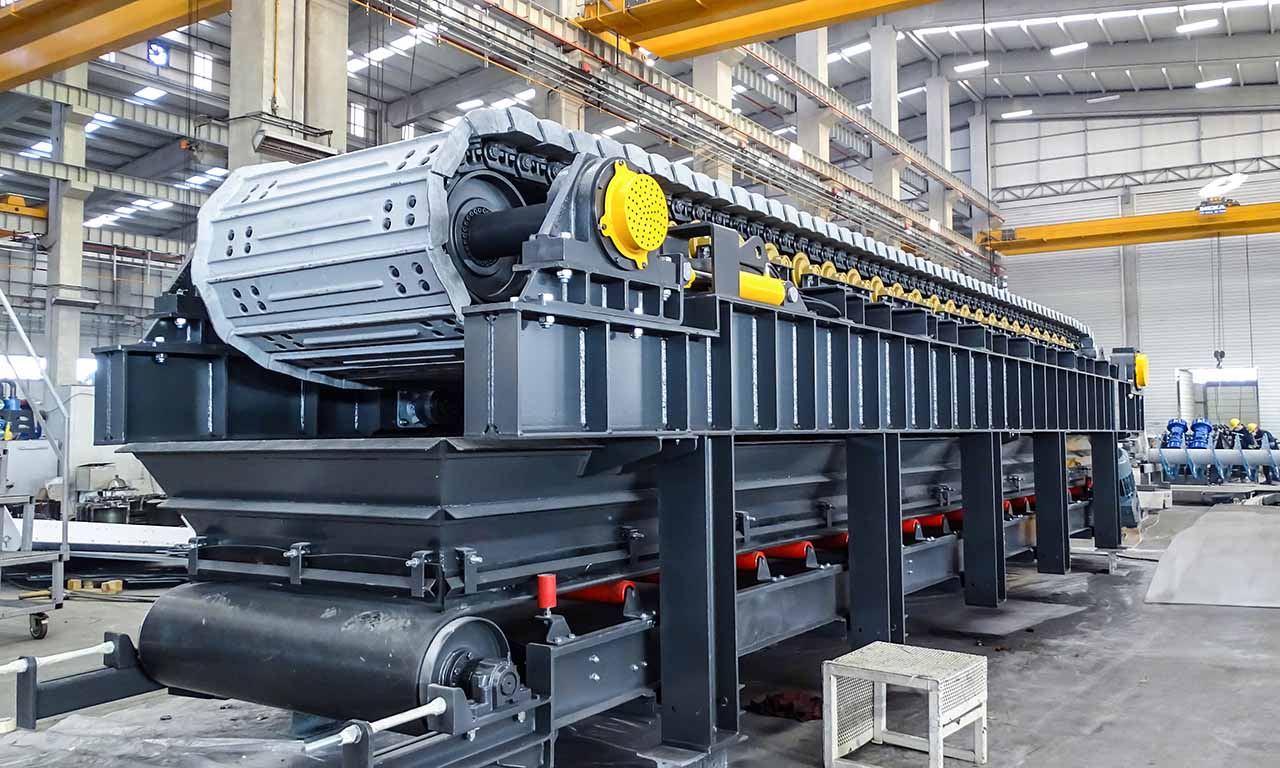
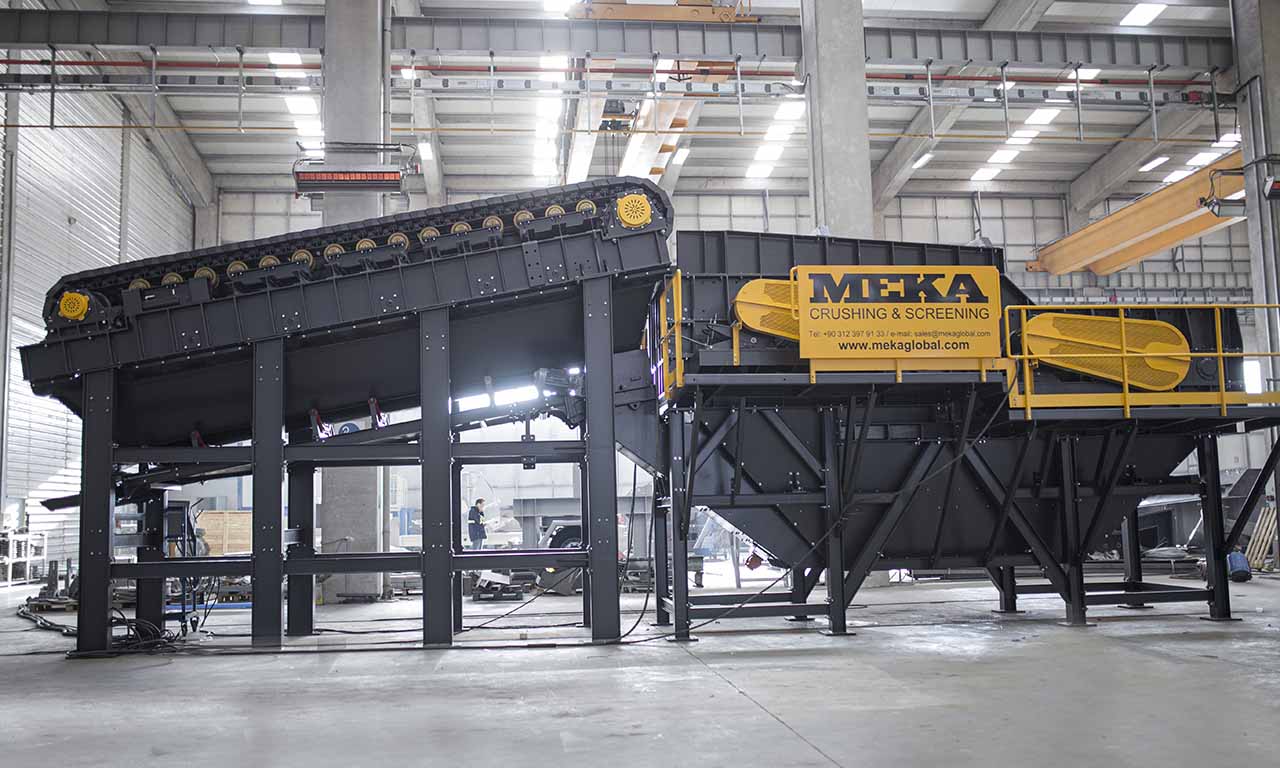
Les alimentateurs MEKA à tablier métallique sont conçus pour ces opérations de manutention exigeantes dans les industries minières, du minerai, du charbon et des granulats. Grâce à leur châssis robuste, leur unité d’entraînement, leurs palettes et leur système de chaînes, ils offrent une durée de vie extrêmement longue et des performances au-delà des attentes.
Applications
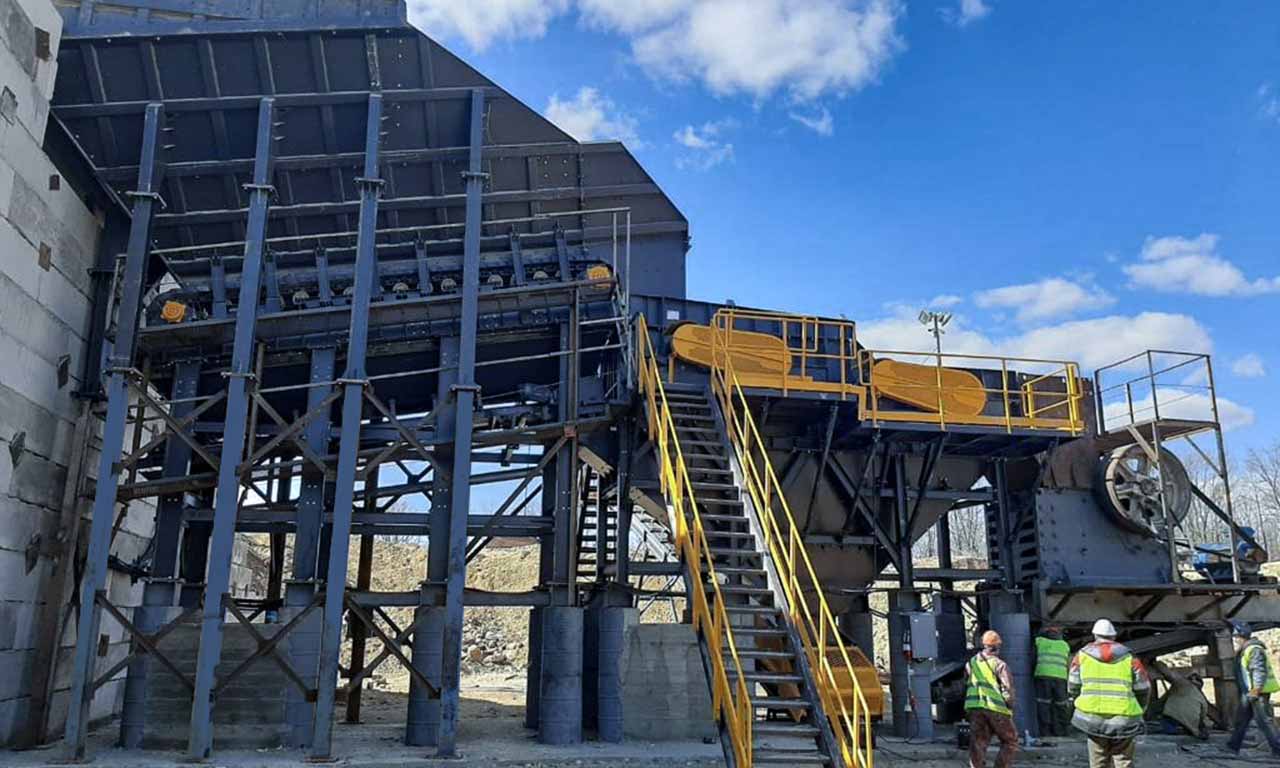
Dans l’exploitation à ciel ouvert et souterraine, pour le transport de matériaux en surface et en sous-sol
Lors d’opérations telles que le chargement/déchargement de camions et de navires, en tant que composant mobile, compact ou stationnaire du système
Déchargement de trémie, étapes de concassage primaire ou secondaire (alimentation du concasseur ou du crible)
Efficacité accrue de l’installation grâce à une alimentation régulière
Alimentateur à Tablier Métallique Spécifications Techniques
| LARGEUR (mm) | *CAPACITÉ (mtph) | VITESSE D'AVANCE MAXIMALE (mm) | VITESSE DE LA CHAÎNE (m/s) | |
| 900 | 110-350 | 380 | 0,1 - 0,30 m/s | |
| 1200 | 230-680 | 520 | 0,1 - 0,30 m/s | |
| 1500 | 350-1100 | 650 | 0,1 - 0,30 m/s | |
| 1800 | 600-1750 | 830 | 0,1 - 0,30 m/s |
*Les chiffres de capacité sont fournis pour : 50 % de profondeur de lit, 0,1-0,3 m/s de vitesse de chaîne et pour un matériau pesant 1,6 t/m³ ou 100 lb/pi³. Les valeurs de capacité sont données à titre indicatif et dépendent non seulement de la taille de l'alimentateur, mais aussi de son inclinaison, de sa granulométrie, etc. D'autres tailles sont également disponibles en fonction de demande.
Souhaitez-vous demander un devis ou recevoir des informations sur un alimentateur à tablier métallique?
Souhaitez-vous recevoir un devis pour un MEKA alimentateur à tablier métallique?
Avez-vous besoin d’un alimentateur à tablier métallique avec des options et configurations différentes ?
Voulez-vous devenir distributeur des MEKA alimentateur à tablier métallique?
Passons au niveau supérieur. Contactez-nous dès maintenant en remplissant le formulaire.