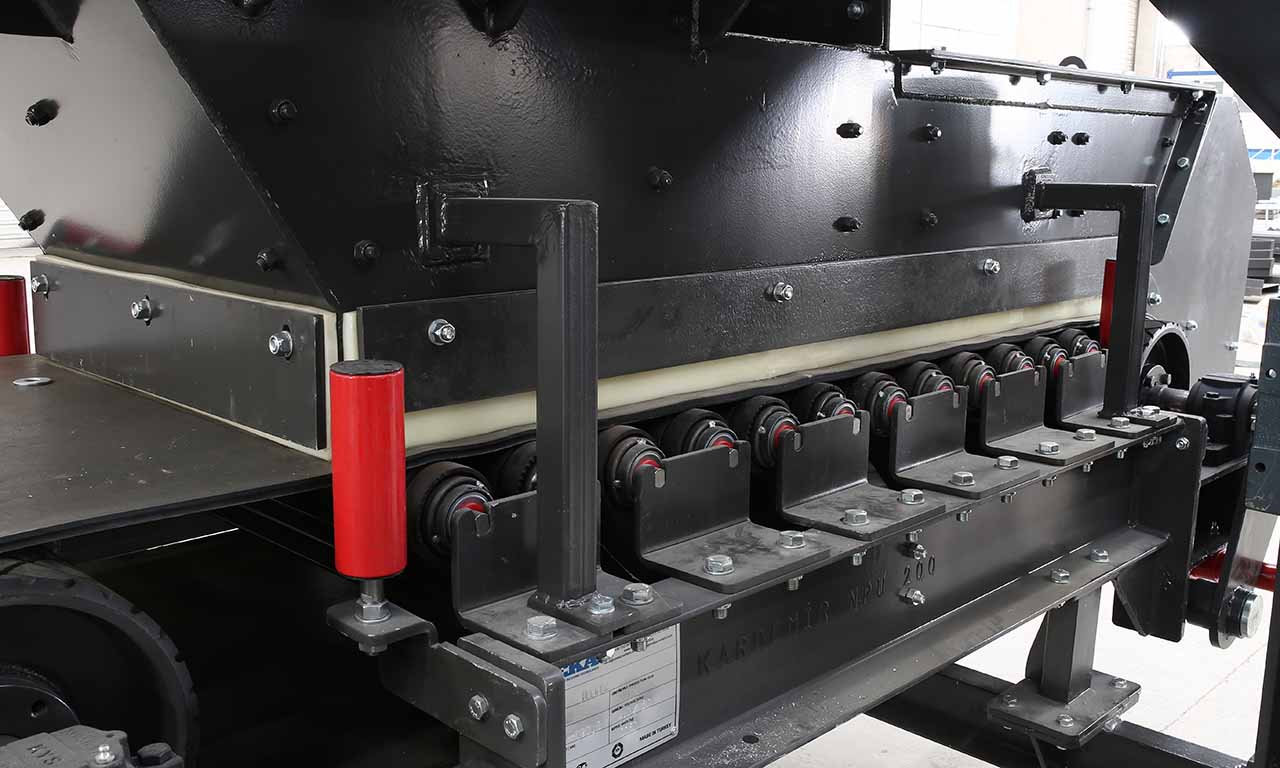
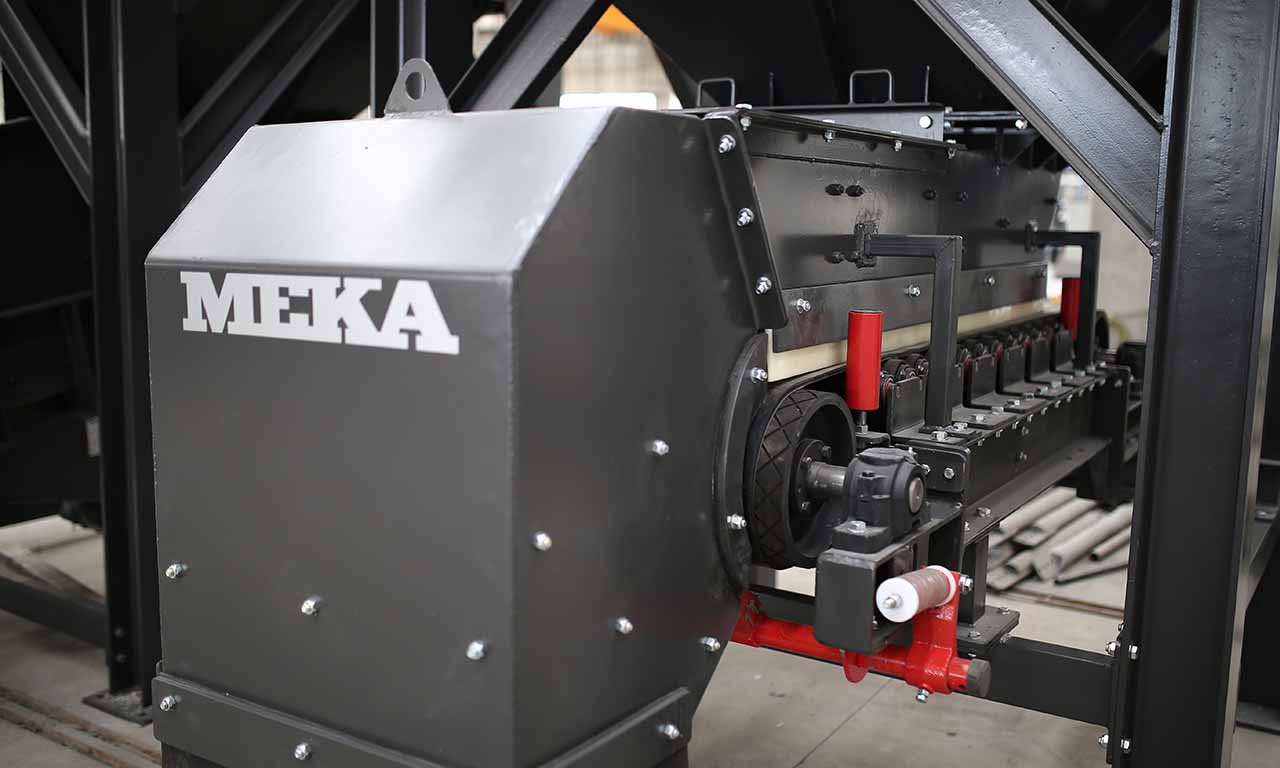
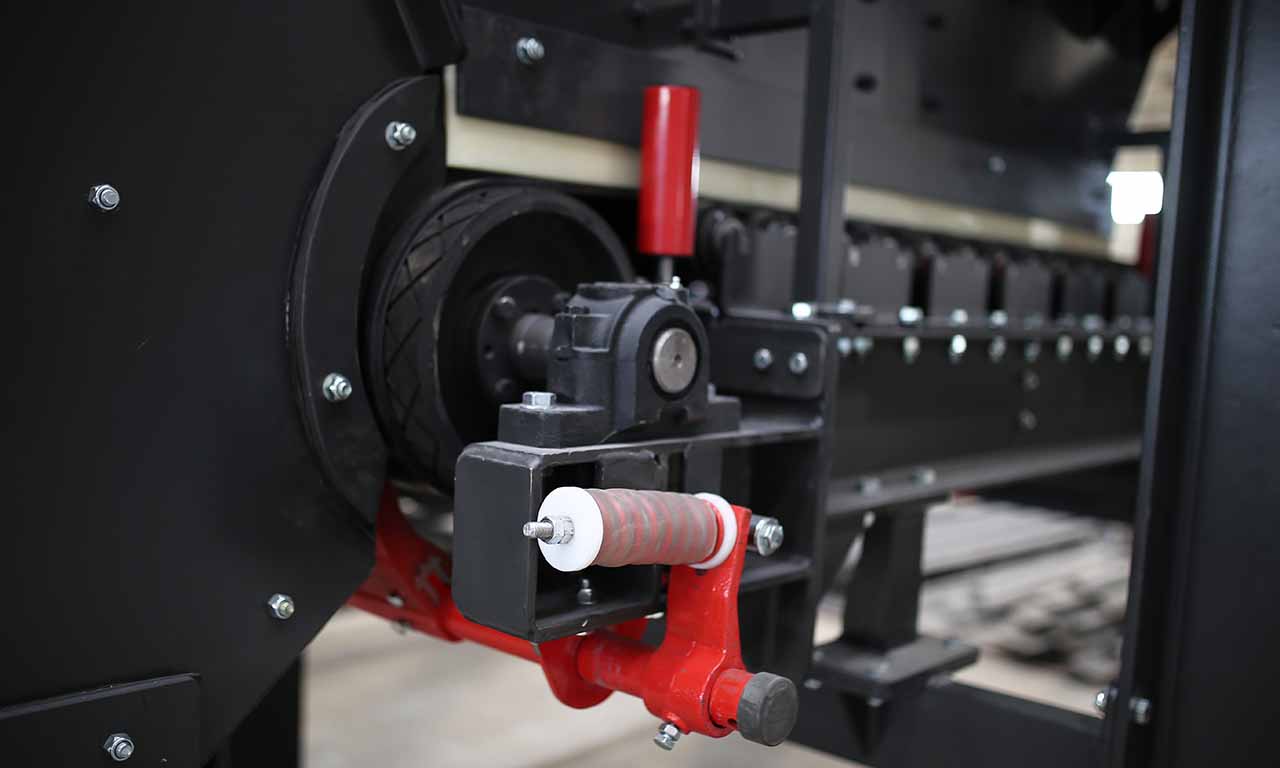
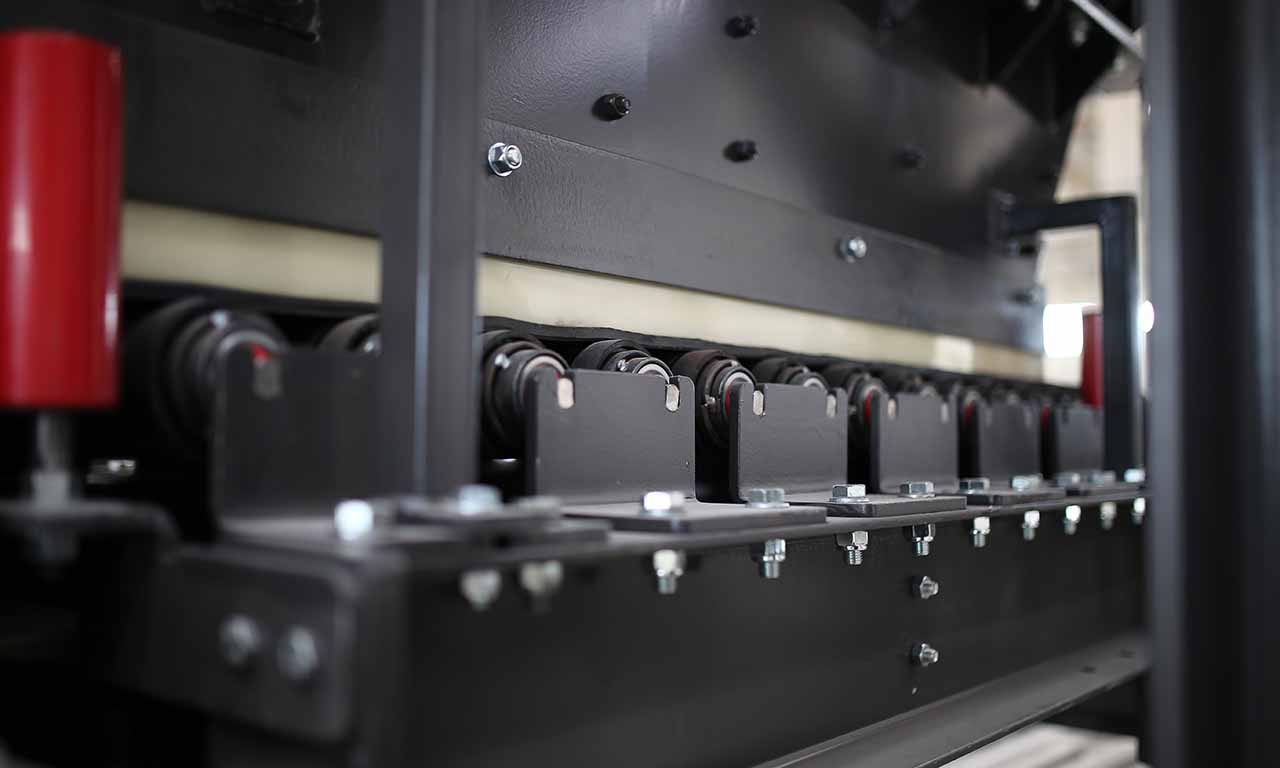
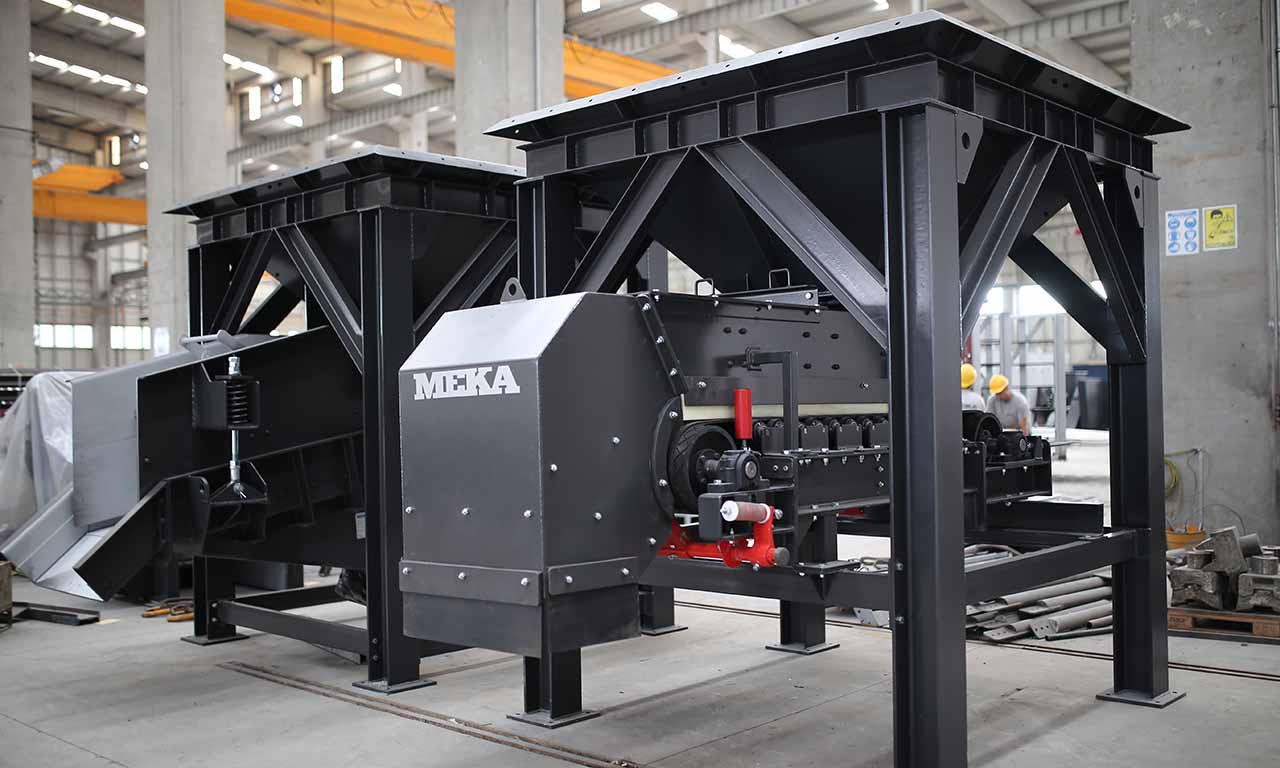
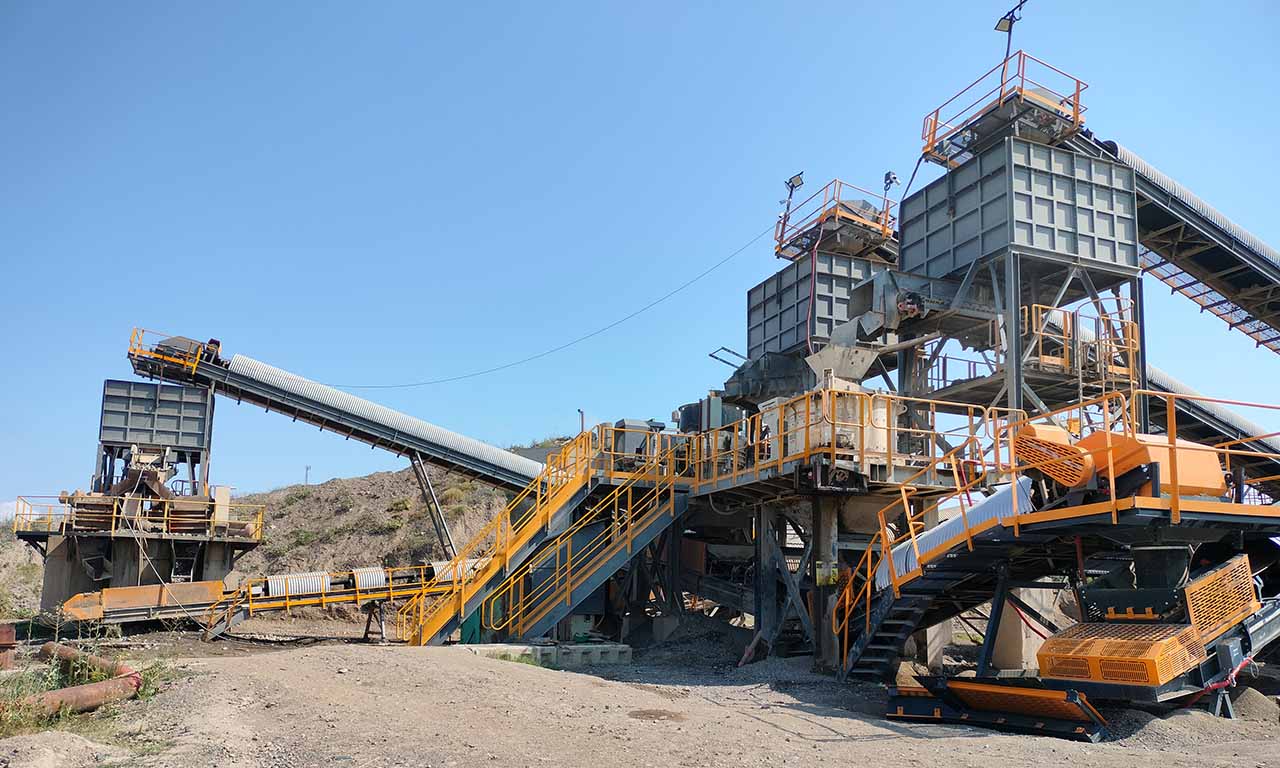
Belt feeders are the type of feeders that perform only feeding function and specifically designed for handling at secondary and tertiary stages.
-
PRODUCTS

-
Ready Mix Concrete Plants
- READY MIX CONCRETE PLANTS HOME
- MOBILE CONCRETE BATCHING PLANTS
- COMPACT CONCRETE BATCHING PLANTS
-
STATIONARY CONCRETE BATCHING PLANTS
- STATIONARY CONCRETE BATCHING PLANTS HOME
- K60 STATIONARY CONCRETE BATCHING PLANT
- K90 STATIONARY CONCRETE BATCHING PLANT
- K120 STATIONARY CONCRETE BATCHING PLANT
- K135 STATIONARY CONCRETE BATCHING PLANT
- K145 STATIONARY CONCRETE BATCHING PLANT
- K160 STATIONARY CONCRETE BATCHING PLANT
- K200 STATIONARY CONCRETE BATCHING PLANT
- DRY BATCH CONCRETE BATCHING PLANTS
- PRECAST CONCRETE BATCHING PLANT
- RCC CONCRETE BATCHING PLANTS
- Concrete Mixers
- Concrete Plants Components
-
After Sales Services and Spare Part
-
Concrete Batching Plant Automation System


MEKA Global has been a leading manufacturer of concrete batching plants, equipment, and crushing and screening solutions -
Ready Mix Concrete Plants
- CORPORATE
- NEWS
- CONTACT
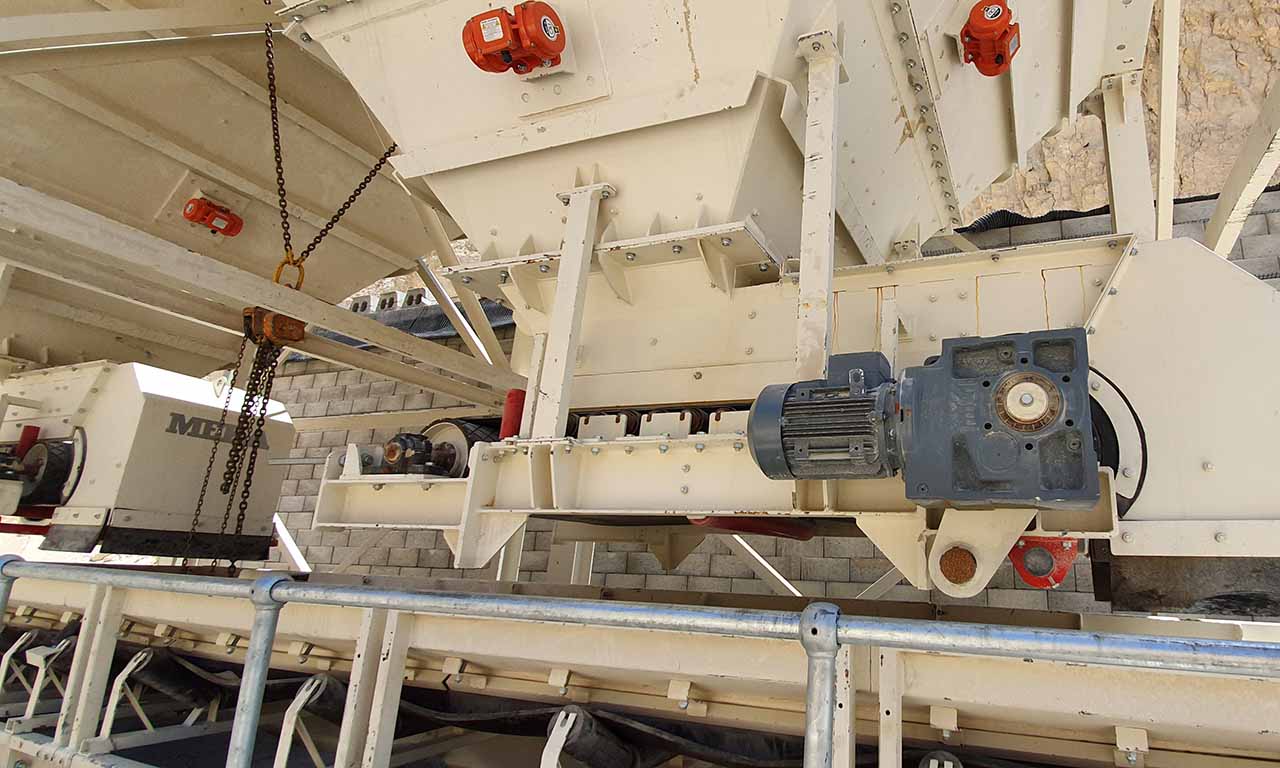
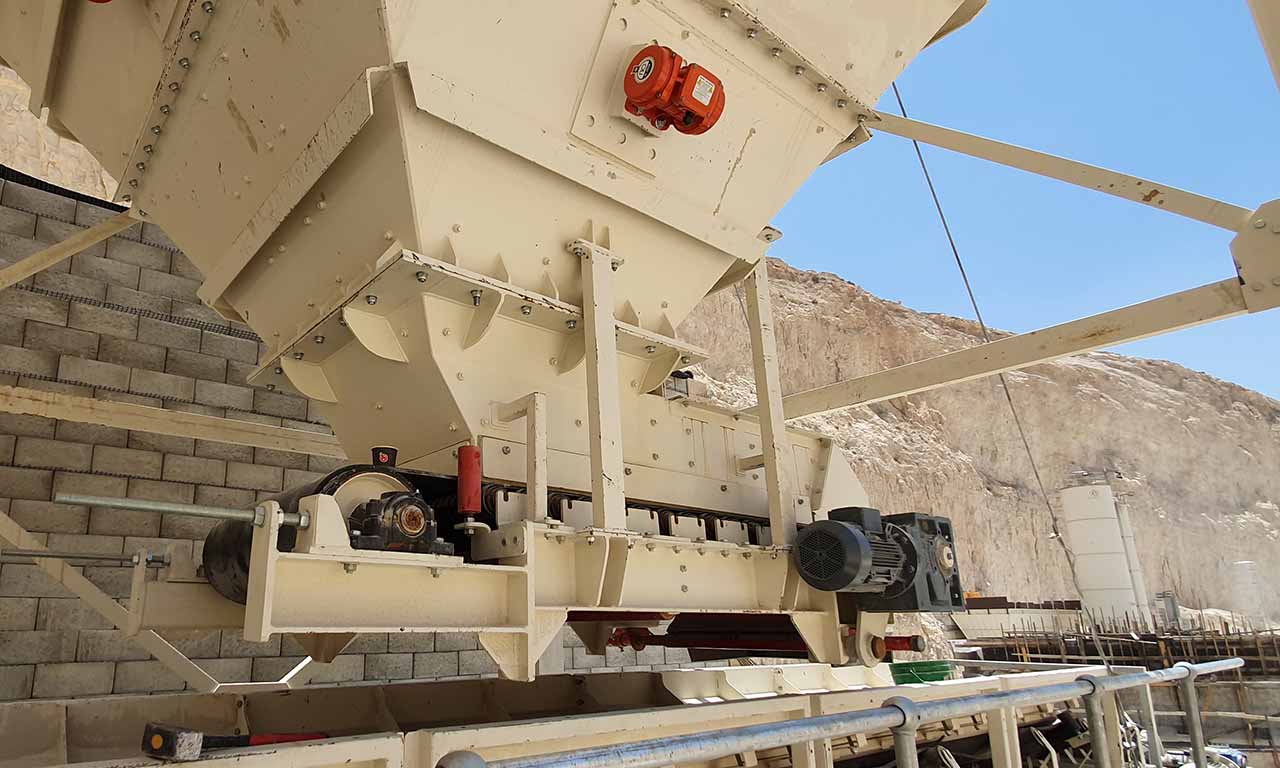
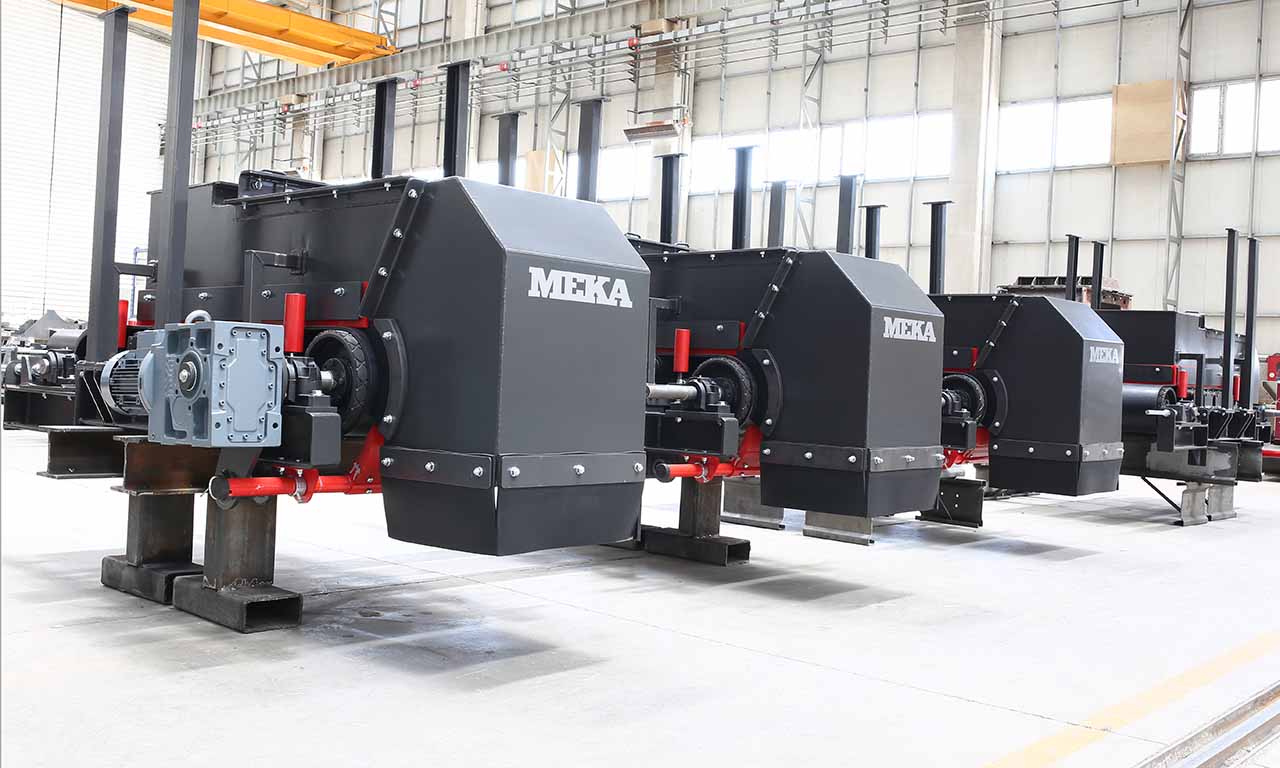
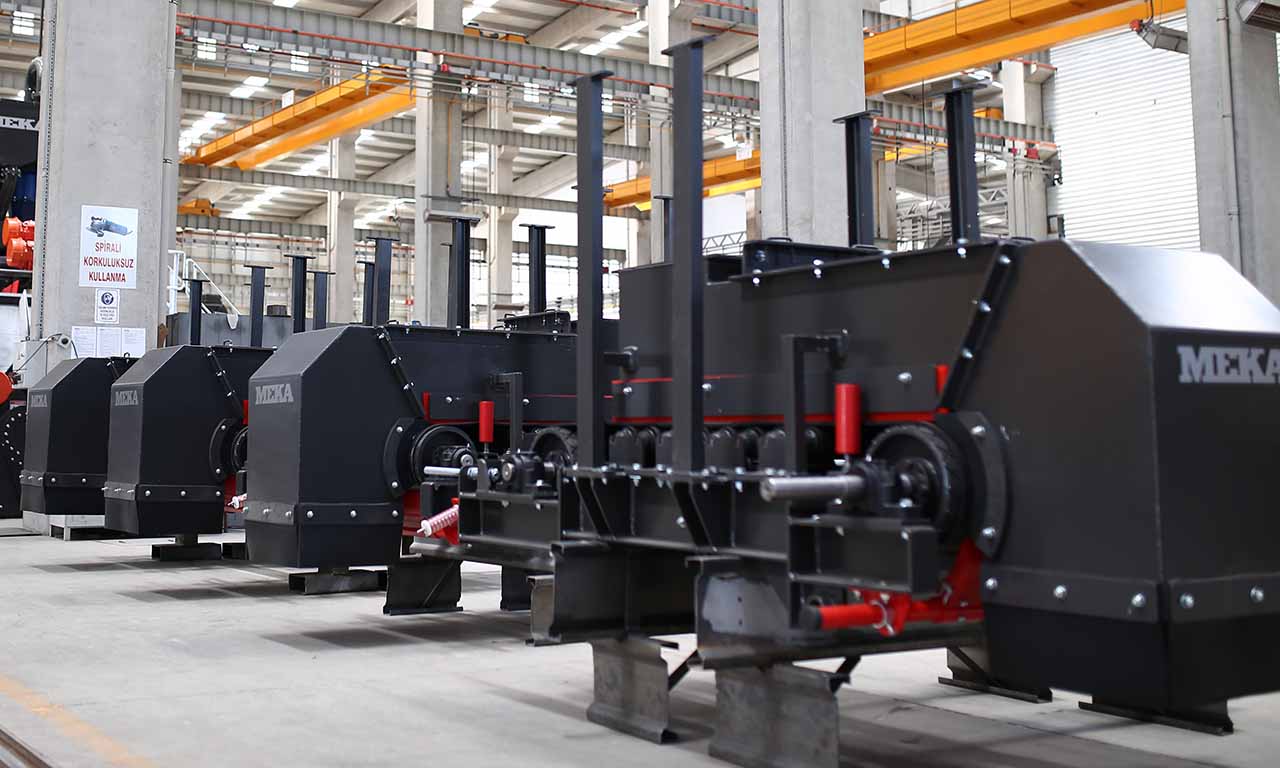
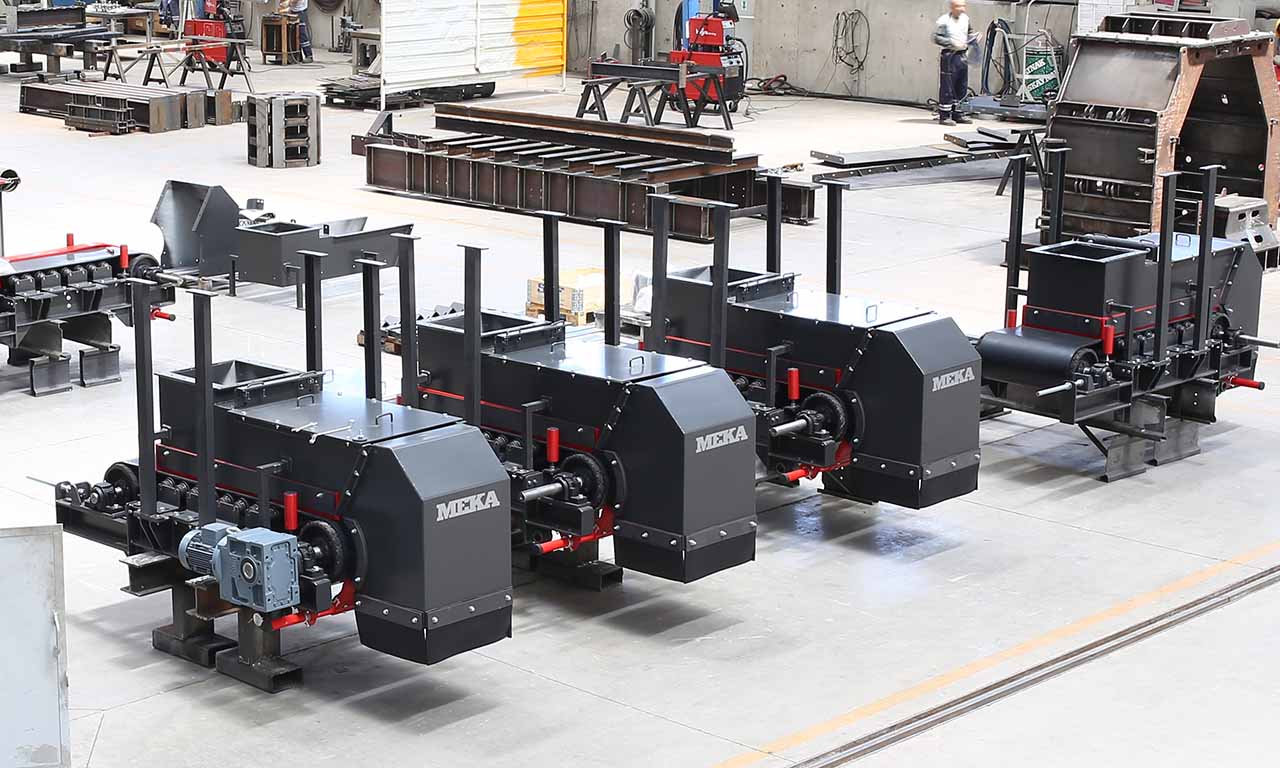
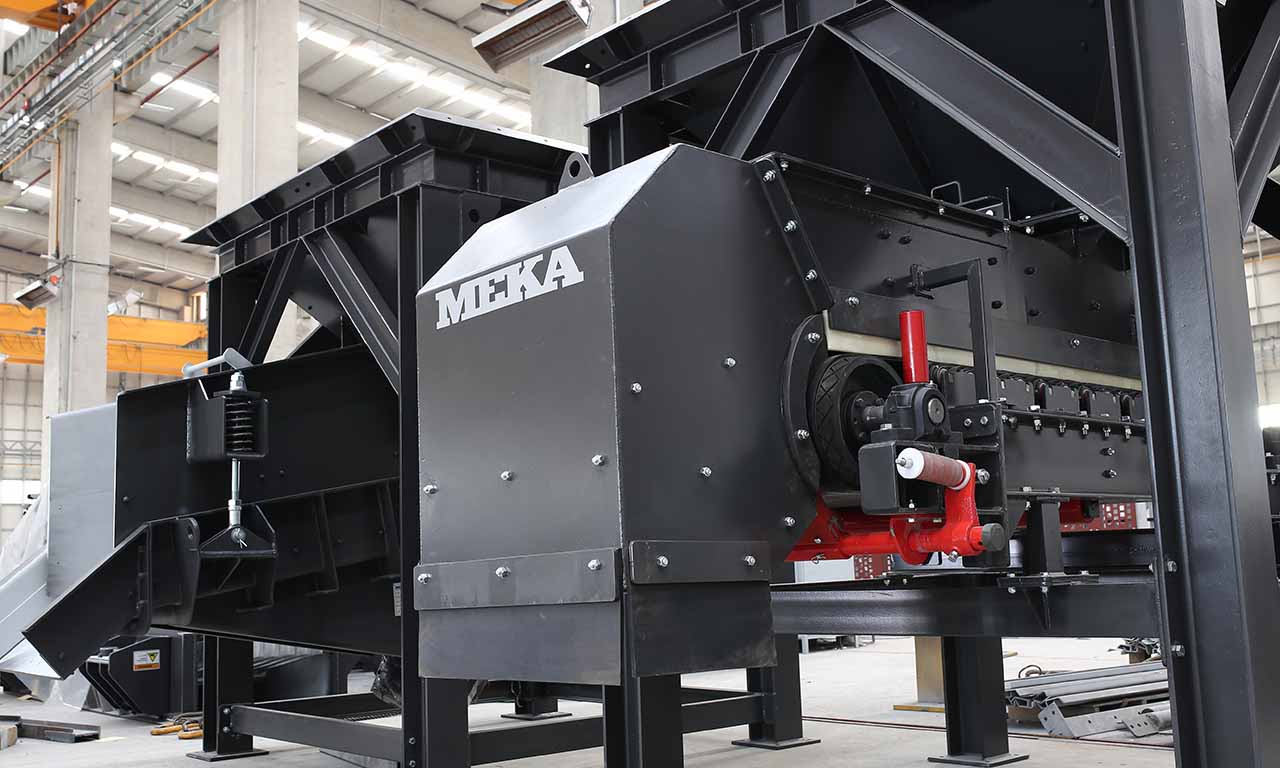
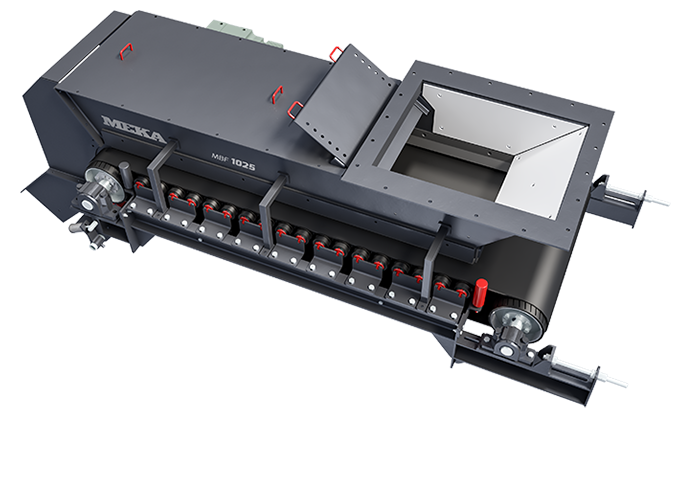
Belt Feeder
Belt Feeder
Belt feeders are short belt conveyors that are specifically designed for material flow regulation, extracting material from one area and ensuring that downstream equipment receives the appropriate volume.
-
MEKA Belt Feeder Download Catalogue
Applications
Belt Feeder Technical Specifications
MBF 6525 |
MBF 8025 |
MBF 1025 |
MBF 1225 |
|
| W x L (mm) W x L (inch x feet) | 650x2500 26x8 | 800x2500 31x8 | 1000x2500 40x8 | 1200x2500 48x8 |
| Power (kW) Power (HP) | 3 4 | 4 5,3 | 5,5 7,4 | 7,5 10 |
| *Capacity (mtph)Capacity (stph)* | 250 272 | 350 385 | 450 495 | 550 606 |
| Belt Speed (m/sec) Belt Speed (fpm) | 0,35 70 | 0,35 70 | 0,35 70 | 0,35 70 |
| Max Feed Size (mm) Max Feed Size (inch x feet) | 100 4 | 150 6 | 150 6 | 150 6 |
*At specified inclination and for material weighing 1.6 t/m³ or 100 lbs/ft³. Capacity values are indicative only and depend not only on feeder size but also on feeder inclination, feed gradation, etc.
What is Belt Feeder?
MEKA Belt Feeders are chosen for their outstanding life characteristics and durability in the harshest conditions.
MEKA has developed belt feeders to suit the most demanding applications in the mining industry and to extract material under dump hoppers or surge bins and to provide the desired, continuous feed rate for screens, crushers, and conveyors.
Types of Belt Feeder
How Does Belt Feeder Work?
Advantages of Using Belt Feeder
Belt Feeder Processes Applications
Driven by an electric motor and gearbox, head drum of feeder move the belt and transport material along the conveyor.
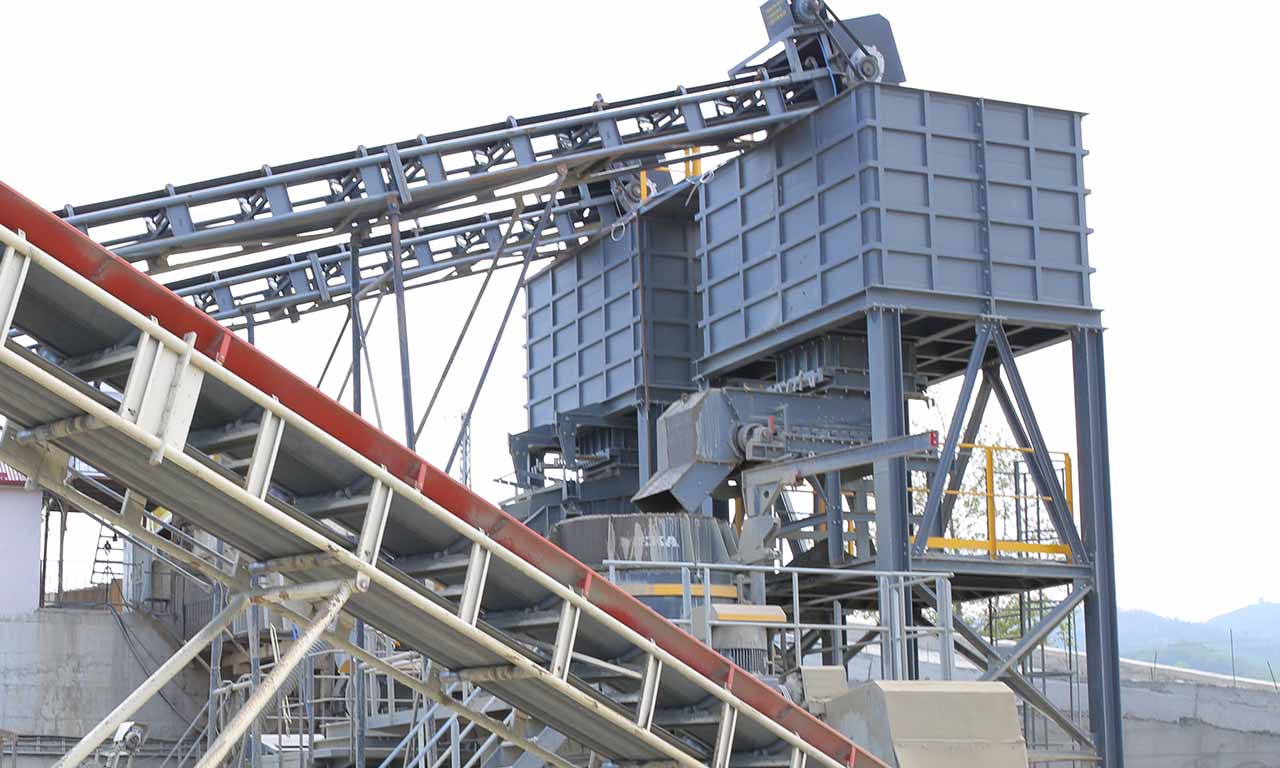
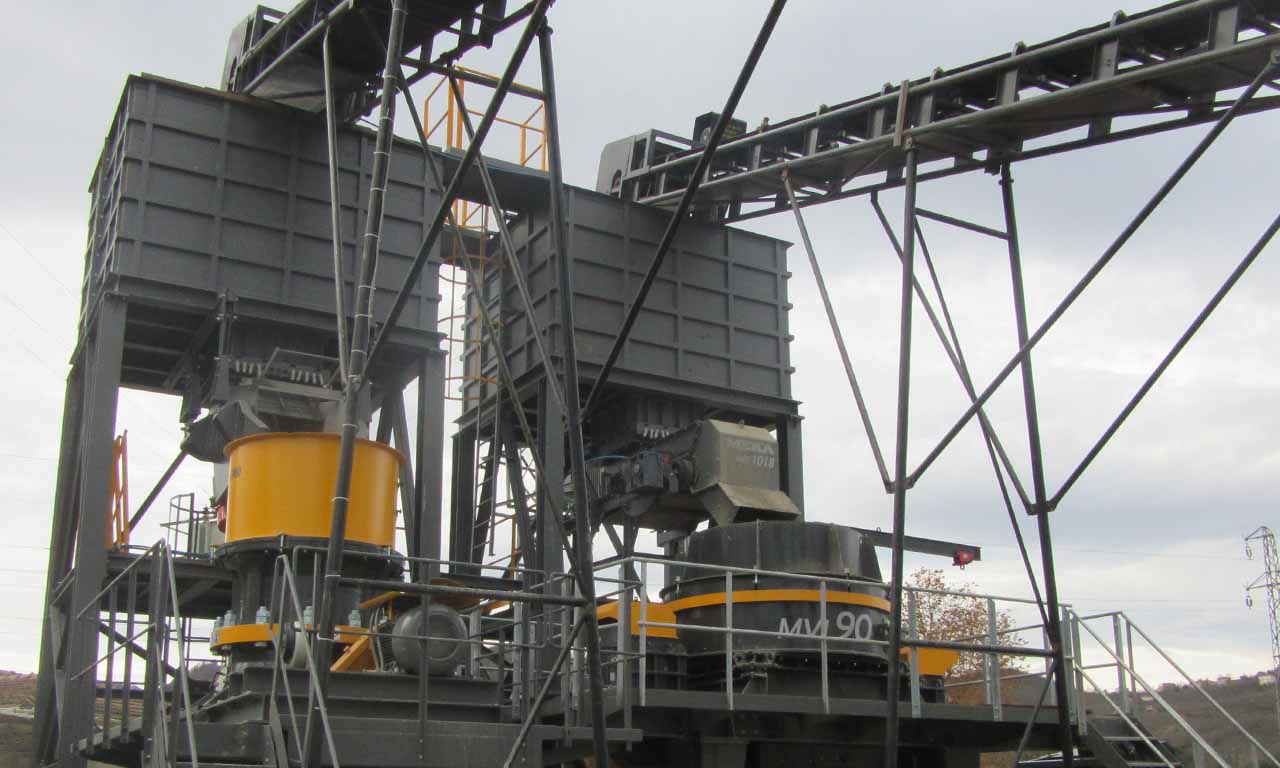
In addition to its different intended uses, it primarily regulates the capacity fluctuations that may occur at the primary stage by ensuring regular feeding of crushers at the secondary and tertiary stages.
Belt feeders are used to feed smoothly flowing materials with a maximum size of 120 mm. They can be used to feed vibrating screens, secondary or tertiary crushers and conventional transport conveyors that require a regular and continuous feed. They are generally mounted horizontally. The end of the belt is located under a bunker or stock chute. Thus, as the material is emptied through the rotation of the belt, the material must be supplied from the bunker above in a continuous flow, without the need for intervention. A vibration motor can be connected to the bunker to prevent blockages in the feeding bunker.
In belt feeders, the rotation speed of the belt is adjusted by means of a power and reducer connection, and the desired feed capacity can be ensured by adjusting the speed. Most of the time, the motion system of the belt feeder is connected to the belt scale on the belt conveyor to which the material is conveyed after the feeder.
Belt feeders are widely used in power plants for feeding coal and ore preparation and enrichment and aggregate production plants, in agriculture, and in any industry where the regular and controlled feed of material below a certain size is required.
In belt feeders, the rotation speed of the belt is adjusted by means of a power and reducer connection, and the desired feed capacity can be ensured by adjusting the speed. Most of the time, the motion system of the belt feeder is connected to the belt scale on the belt conveyor to which the material is conveyed after the feeder.
Belt feeders are widely used in power plants for feeding coal and ore preparation and enrichment and aggregate production plants, in agriculture, and in any industry where the regular and controlled feed of material below a certain size is required.